Slo-Niacin
23 June, 2023
Sodium Bicarbonate Infant Injection
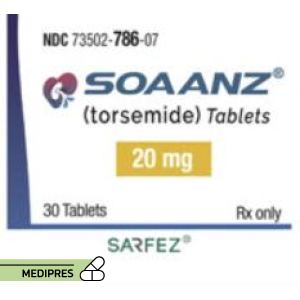
23 June, 2023Soaanz
Generic name: Torsemide
Drug class: Loop diuretics
Dosage form: Tablets
Route of administration: Oral
Dose: The recommended initial dose is 20 mg orally once daily. If the diuretic response is inadequate, titrate upward by approximately doubling the dose until the desired diuretic response is obtained. Doses higher than 200 mg have not been adequately studied.
Mechanism of action: Torsemide inhibits the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidneys, leading to increased excretion of sodium, chloride, and water, thereby reducing fluid accumulation in the body.
Drug usage cases:
- Treatment of edema associated with heart failure
- Treatment of edema associated with renal disease
- Treatment of edema associated with hepatic disease
- Management of hypertension
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to torsemide
- Anuria (inability to urinate)
- Hepatic coma
Side effects:
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Electrolyte imbalances, including hypokalemia (low potassium), hyponatremia (low sodium), hypomagnesemia (low magnesium), hypocalcemia (low calcium), and hypochloremic alkalosis
- Ototoxicity (hearing damage), especially with high doses or rapid intravenous administration
- Renal impairment
- Elevated blood glucose levels
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting
- Rash
- Fatigue
Warnings:
- Monitor blood pressure regularly due to the risk of hypotension
- Regularly assess renal function and electrolyte levels to detect potential imbalances
- Use caution in patients with a history of hearing impairment due to the risk of ototoxicity
- Monitor blood glucose levels, especially in diabetic patients, as torsemide may elevate blood sugar
- Use with caution in patients with a history of gout, as torsemide may increase uric acid levels
- Be cautious when administering torsemide to patients with hepatic disease, as it may exacerbate hepatic encephalopathy
- Use caution in elderly patients, who may be more sensitive to the effects of torsemide
- Monitor for signs of dehydration, as excessive diuresis can lead to volume depletion
- Be aware of potential interactions with other medications, such as NSAIDs, lithium, and other diuretics
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: The safety of torsemide during pregnancy has not been established. It should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It is not known whether torsemide is excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when administering torsemide to a nursing woman, and a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.