Loperamide
23 June, 2023
Losartan
23 June, 2023Lorazepam
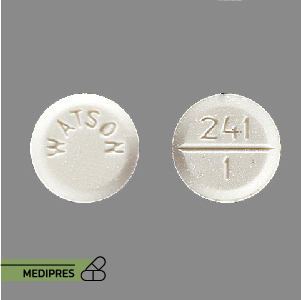
Generic name: Lorazepam
Drug classes: Benzodiazepine anticonvulsants, Benzodiazepines, Miscellaneous antiemetics
Dosage forms: Capsule, Extended release, Concentrate, Tablet
Root of administration: Oral
Dose: Capsule, extended release :1, 1.5, 2,3 mg, Concentrate: 2 mg/mL, Tablet: 0.5,1,2 mg
Mechanism of action: Lorazepam belongs to a class of medications called benzodiazepines. It is thought that benzodiazepines work by enhancing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain.
Drug usage cases: Lorazepam is used in adults and children at least 12 years old to treat anxiety disorders. Loreev XR extended-release capsules are used to treat anxiety disorders in adults only. Lorazepam is also used to treat insomnia caused by anxiety or temporary situational stress. Lorazepam is sometimes used to treat nausea and vomiting from cancer treatment and to control agitation caused by alcohol withdrawal.
Drug contra indications: You should not use lorazepam if you have:
narrow-angle glaucoma; or a history of allergic reaction to any benzodiazepine (alprazolam, diazepam, Valium, Xanax, Versed, Klonopin, and others). To make sure lorazepam is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had:
asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sleep apnea, or other breathing disorder;
drug or alcohol addiction; depression, mental illness or psychosis, mood changes, or suicidal thoughts or actions; seizures; an allergy to aspirin or yellow food dye; or kidney or liver disease.
side effects: Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to lorazepam: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Lorazepam can slow or stop your breathing, especially if you have recently used an opioid medication or alcohol. A person caring for you should seek emergency medical attention if you have slow breathing with long pauses, blue colored lips, or if you are hard to wake up. Lorazepam may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have:
severe drowsiness; unusual changes in mood or behavior, being agitated or talkative; sudden restless feeling or excitement; seizures, depression, thinking problems, thoughts of suicide or hurting yourself; confusion, aggression, hallucinations; sleep problems (insomnia); vision changes; or dark urine, or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes). Drowsiness or dizziness may last longer in older adults. Use caution to avoid falling or accidental injury.
Warnings: Lorazepam can slow or stop your breathing, especially if you have recently used an opioid medication, alcohol, or other drugs that can slow your breathing. These effects can be fatal. MISUSE CAN CAUSE ADDICTION, OVERDOSE, OR DEATH. Keep this medicine where others cannot get to it. Lorazepam may be habit-forming and should be used only by the person it was prescribed for. This medicine should never be shared with another person, especially someone who has a history of drug abuse or addiction. Do not stop using lorazepam without asking your doctor. You may have life-threatening withdrawal symptoms if you stop using the medicine suddenly after long-term use. Some withdrawal symptoms may last up to 12 months or longer. Get medical help right away if you stop using lorazepam and have symptoms such as: unusual muscle movements, being more active or talkative, sudden and severe changes in mood or behavior, confusion, hallucinations, seizures, or thoughts about suicide. You should not use this medicine if you have narrow-angle glaucoma, severe respiratory insufficiency, myasthenia gravis, or if you are allergic to Valium or a similar medicine.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Do not use lorazepam if you are pregnant. This medicine can cause birth defects or life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in a newborn. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. If you use lorazepam during pregnancy, your baby could be born with life-threatening withdrawal symptoms, and may need medical treatment for several weeks. If you are pregnant, your name may be listed on a pregnancy registry to track the effects of lorazepam on the baby. You should not breastfeed. If you do breastfeed, tell your doctor if you notice drowsiness, feeding problems, or slow weight gain in the nursing baby.