Prozac
23 June, 2023
Qelbree
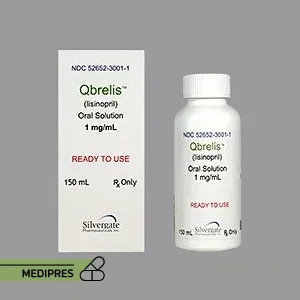
23 June, 2023Qbrelis
Generic name: lisinopril [ lyse-IN-oh-pril ]
Brand names: Prinivil, Qbrelis, Zestril
Drug class: Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Dosage forms: Oral solution.
Route of administration: Oral.
Dose: Hypertension: Starting dose is 10 mg once daily. Typical dose ranges from 20 mg to 40 mg once daily. Heart failure: Starting dose is 5 mg once daily. Typical dose ranges from 5 mg to 20 mg once daily. Acute myocardial infarction: 5 mg within 24 hours of symptom onset, followed by 5 mg after 24 hours, then 10 mg once daily.
Mechanism of action: Lisinopril works by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which is responsible for converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure. By reducing the production of angiotensin II, lisinopril relaxes blood vessels, lowers blood pressure, and decreases the workload on the heart.
Drug usage cases: Treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure) in adults and children aged 6 years and older. Management of heart failure. Improvement of survival following acute myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Drug contraindications: Known hypersensitivity to lisinopril or any component of the formulation. History of angioedema related to previous treatment with an ACE inhibitor. Hereditary or idiopathic angioedema. Concomitant use with aliskiren in patients with diabetes.
Side effects: Common: Dizziness, headache, cough, fatigue, nausea. Serious: Angioedema (swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat), hyperkalemia (high potassium levels), hypotension (low blood pressure), renal impairment. Rare: Liver dysfunction, jaundice, severe allergic reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Warnings: Monitor blood pressure, renal function, and electrolytes regularly during treatment. Use with caution in patients with renal impairment, liver disease, or a history of angioedema. Avoid using potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics unless directed by your doctor. Inform your doctor if you experience symptoms of angioedema, such as swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, or difficulty breathing. Be aware of potential interactions with other medications that affect blood pressure, renal function, or potassium levels.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Contraindicated during pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus (ACE inhibitors can cause injury and death to the developing fetus). Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception. Lisinopril may be excreted in breast milk. Consult your doctor before using this medication while breastfeeding.