Seroquel
23 June, 2023Simethicone
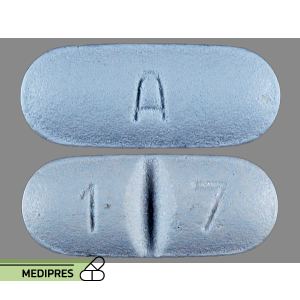
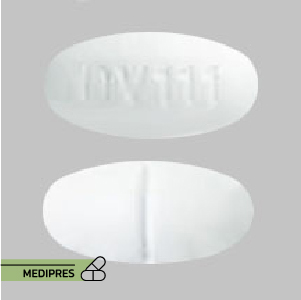
23 June, 2023Sertraline
Generic name: Sertraline
Drug class: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
Dosage form: Tablets (25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg), Liquid (20 mg/mL)
Root of administration: Oral
Dose: Initial dose: 25 mg to 50 mg once daily; Maintenance dose: 50 mg to 200 mg once daily; Maximum recommended dose: 200 mg per day.
Mechanism of action: Sertraline inhibits the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, increasing serotonin levels and enhancing neurotransmission, which helps improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Drug usage cases:
- Major depressive disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Panic disorder
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
- Social anxiety disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Premature ejaculation (off-label)
Drug contraindications:
- Concurrent use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Hypersensitivity to sertraline or any of its components
- Concurrent use with pimozide
- Concurrent use with disulfiram (for sertraline concentrate due to ethanol content)
Side effects:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia
- Somnolence
- Dizziness
- Tremor
- Headache
- Sexual dysfunction (e.g., decreased libido, ejaculation failure)
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Restless legs syndrome
- Excessive sweating
- Weight changes (minimal weight gain reported)
- Suicidal thoughts (increased risk in individuals under 25 years old)
Warnings:
- Risk of serotonin syndrome, especially when combined with other serotonergic agents
- Potential for increased suicidal thoughts and behaviors in individuals under 25 years old
- Use with caution in patients with liver impairment; dosage adjustments may be necessary
- Discontinuation should be gradual to minimize withdrawal symptoms
- Monitor for signs of bleeding, especially when used with NSAIDs or anticoagulants
- May cause QT interval prolongation; use with caution in patients with cardiac conditions
- Risk of hyponatremia, particularly in elderly patients
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Pregnancy: Sertraline is classified as Category C by the FDA, indicating that risk to the fetus cannot be ruled out. Studies have shown an increased risk of congenital heart defects in newborns exposed to sertraline during pregnancy. Therefore, sertraline should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Breastfeeding: Sertraline is excreted in human milk. While the amount transferred to the infant is relatively low, caution is advised when administering sertraline to nursing mothers. The decision to continue breastfeeding or discontinue the drug should be made based on the importance of the medication to the mother and the potential risks to the infant.