Bisacodyl Suppository
23 June, 2023
Brisdelle
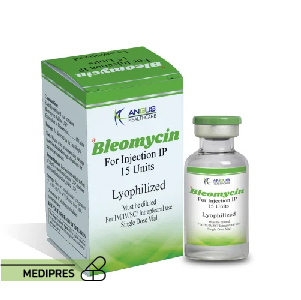
23 June, 2023Bleomycin
Generic name: bleomycin [ BLEE-oh-MYE-sin ]
Brand names: Blenoxane, Bleo 15k
Drug class: Antineoplastic antibiotic
Dosage form: Injectable solution
Route of administration: Intravenous (IV), Intramuscular (IM), Subcutaneous (SC), Intrapleural
Available Dose: Typically supplied as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution in vials of 15 units or 30 units.
Mechanism of action: Bleomycin binds to DNA, causing strand breaks and inhibition of DNA synthesis and function, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. It is believed to exert its effects primarily through the formation of free radicals.
Drug usage cases: Bleomycin is primarily used in the treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, testicular cancer, and certain types of squamous cell carcinomas. It is also used in the treatment of pleural effusions caused by malignancy, as a sclerosing agent.
Drug contra indications: Contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to bleomycin or any component of the formulation, and in patients with severe lung function impairment.
Side effects: Common side effects include skin reactions, fever, and chills. Pulmonary toxicity is a significant concern and may manifest as pneumonitis or pulmonary fibrosis. Other side effects can include changes in skin pigmentation, hair loss, mucositis, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
Warnings: Patients should be monitored for pulmonary function before and during treatment. Renal function monitoring is also advised as the drug is primarily excreted through the kidneys. Avoiding exposure to oxygen at high concentrations for long periods is recommended to reduce the risk of pulmonary toxicity.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Bleomycin is classified as FDA pregnancy category D. It should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It is unknown whether bleomycin is excreted in human milk; caution should be exercised when administered to breastfeeding women.
Bleomycin plays a vital role in cancer chemotherapy, especially in combination regimens. However, its use requires careful monitoring due to the risk of severe side effects, particularly pulmonary toxicity.