Butalbital, Acetaminophen and Caffeine Capsule
23 June, 2023
Cabergoline
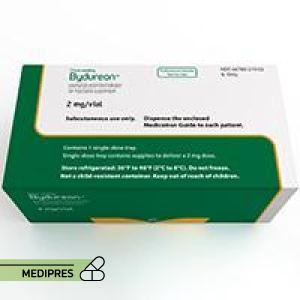
23 June, 2023Bydureon Pen
Generic name: exenatide
Drug class: GLP-1 receptor agonist
Dosage form: pre-filled pen injector
Root of administration: subcutaneous injection
Dose: 2 mg once weekly
Mechanism of action: exenatide mimics the action of incretin hormones, enhancing insulin secretion in response to meals, inhibiting glucagon release, and slowing gastric emptying, thereby improving glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients.
Drug usage cases:
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus: used as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults.
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to exenatide or any component of the formulation.
- Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma.
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2.
- Severe gastrointestinal disease, including gastroparesis.
- End-stage renal disease or severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m²).
Side effects:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Injection site reactions (e.g., redness, swelling, itching)
- Hypoglycemia (when used with sulfonylureas or insulin)
- Pancreatitis (rare)
- Thyroid tumors (observed in animal studies; relevance to humans unknown)
Warnings:
- Monitor renal function regularly; discontinue if renal impairment worsens.
- Assess for signs of pancreatitis; discontinue if suspected.
- Use caution in patients with a history of gallbladder disease.
- Not recommended for use with insulin; concurrent use has not been studied.
- Not recommended for patients with type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Discontinue if a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs.
- Use caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Exenatide is classified as a pregnancy category C drug, indicating that risk to the fetus cannot be ruled out. It should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It is not known whether exenatide is excreted in human milk; caution should be exercised when administering to a nursing woman. The decision to discontinue nursing or the drug should be made based on the importance of the drug to the mother.