Cetuximab
23 June, 2023
Chlorhexidine
23 June, 2023Chlordiazepoxide
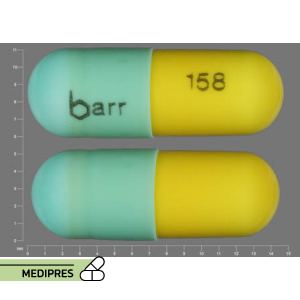
Generic name: Chlordiazepoxide
Drug class: Benzodiazepines
Dosage form: Oral capsule (5 mg, 10 mg, 25 mg)
Root of administration: Oral
Dose:
- Adults:
- Relief of mild and moderate anxiety disorders and symptoms of anxiety: 5 mg or 10 mg, 3 or 4 times daily
- Relief of severe anxiety disorders and symptoms of anxiety: 20 mg or 25 mg, 3 or 4 times daily
- Preoperative apprehension and anxiety: 5 to 10 mg orally, 3 or 4 times daily; if used as preoperative medication, 50 to 100 mg intramuscularly 1 hour prior to surgery
- Geriatric patients or in the presence of debilitating disease: 5 mg, 2 to 4 times daily
- Pediatric patients: 5 mg, 2 to 4 times daily (may be increased in some pediatric patients to 10 mg, 2 to 3 times daily); not recommended for children under 6 years of age
Mechanism of action: Chlordiazepoxide enhances the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, leading to a calming effect on the central nervous system.
Drug usage cases:
- Short-term treatment of anxiety disorders
- Management of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms
- Preoperative apprehension and anxiety
- Adjunctive treatment for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) when combined with clidinium bromide
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to chlordiazepoxide or other benzodiazepines
- Acute narrow-angle glaucoma
- Severe liver impairment (e.g., hepatitis, cirrhosis)
- Myasthenia gravis
- Severe respiratory insufficiency
- Sleep apnea syndrome
- Concurrent use with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants
Side effects:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Ataxia (lack of muscle coordination)
- Blurred vision
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (e.g., nausea, constipation)
- Skin rash
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Respiratory depression (especially when combined with other CNS depressants)
- Dependence and withdrawal symptoms with prolonged use
Warnings:
- Risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms with prolonged use; taper dosage gradually under medical supervision
- Use caution in elderly patients due to increased sensitivity and risk of sedation
- Monitor liver function in patients with hepatic impairment
- Avoid concurrent use with alcohol and other CNS depressants to prevent additive sedative effects
- May impair mental and physical abilities; avoid operating heavy machinery until effects are known
- Use during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus; not recommended during breastfeeding
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Chlordiazepoxide is classified as a Category D medication during pregnancy, indicating that there is positive evidence of human fetal risk. It should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Chlordiazepoxide is excreted in breast milk and may cause sedation and respiratory depression in a nursing infant. Therefore, it is not recommended for use during breastfeeding. Alternative treatments should be considered for pregnant or breastfeeding women.