Aspirin and Omeprazole Tablets
23 June, 2023
Atarax
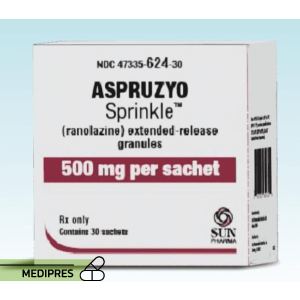
23 June, 2023Aspruzyo Sprinkle
Generic name: ranolazine
Drug class: Antianginal agents
Dosage form: Oral granules
Root of administration: Oral
Dose: 500 mg orally twice daily; may increase to 1000 mg orally twice daily based on clinical symptoms. The maximum recommended daily dose is 2000 mg (1000 mg twice daily). If a dose is missed, take the prescribed dose at the next scheduled time; do not double the next dose.
Mechanism of action: Ranolazine inhibits late sodium currents in cardiac myocytes, reducing intracellular calcium overload and decreasing myocardial oxygen consumption, thereby improving exercise tolerance and reducing angina frequency.
Drug usage cases:
- Chronic angina
Drug contraindications:
- Severe hepatic impairment (cirrhosis)
- Concurrent use with strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin) or inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin)
- Concurrent use with drugs that prolong the QT interval (e.g., certain antiarrhythmics, antipsychotics, antidepressants)
Side effects:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Constipation
- Nausea
- QT interval prolongation (may lead to arrhythmias)
- Elevated blood pressure
- Peripheral edema
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
Warnings:
- Monitor ECG for QT interval prolongation
- Use caution in patients with renal impairment; dose adjustment may be necessary
- Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice during treatment
- Use caution when driving or operating machinery until the drug’s effects are known
- Alcohol may increase the risk of side effects; avoid alcohol during treatment
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: The safety of ranolazine during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established. Use during pregnancy should be considered only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. It is not known whether ranolazine is excreted in human milk; caution should be exercised when administering to a nursing woman.