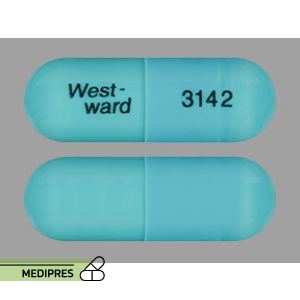
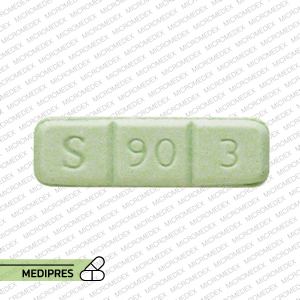
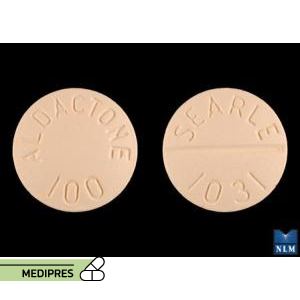
Ativan (Lorazepam Oral)
23 June, 2023
Atropine and diphenoxylate
23 June, 2023Atridox
Generic name: doxycycline hyclate
Drug class: tetracycline antibiotic
Dosage form: subgingival controlled-release gel
Root of administration: subgingival application
Dose: a single application of 50 mg doxycycline hyclate per periodontal pocket
Mechanism of action: doxycycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by disrupting transfer RNA and messenger RNA at ribosomal sites, leading to bacteriostatic effects. It is effective against periodontal pathogens such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Campylobacter rectus, and Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Drug usage cases:
- Treatment of chronic adult periodontitis to achieve a gain in clinical attachment, reduction in probing depth, and reduction in bleeding on probing.
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to doxycycline or any other tetracycline antibiotic.
- Use during tooth development (last half of pregnancy, infancy, and childhood up to the age of eight years) due to the risk of permanent discoloration of teeth and enamel hypoplasia.
- Pregnancy, as tetracyclines can cross the placenta and may cause fetal harm.
- Breastfeeding, as doxycycline is excreted into human milk and may affect the nursing infant.
Side effects:
- Gum discomfort, pain, or soreness.
- Loss of tooth attachment.
- Increased pocket depth.
- Toothache.
- Pressure sensitivity.
- Periodontal abscess.
- Exudate.
- Infection.
- Drainage.
- Extreme mobility.
- Suppuration.
- Thermal tooth sensitivity.
- Gum inflammation, swelling, or erythema.
- Sore mouth.
- Indigestion or upset stomach.
- Diarrhea.
- Tooth mobility.
- Bone loss.
- Periapical abscess.
- Aphthous ulcers or canker sores.
- Fistula.
- Endodontic abscess.
- Pulpitis.
- Jaw pain.
- Tooth loss.
- Broken tooth.
- Bleeding gums.
Warnings:
- Photosensitivity reactions, including exaggerated sunburn, may occur; patients should be advised to avoid direct sunlight or ultraviolet light exposure during treatment.
- Potential for overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi; prolonged use may lead to superinfections.
- Use with caution in patients with a history of or predisposition to oral candidiasis.
- Not evaluated in patients with severe periodontal defects or immunocompromised conditions; safety and efficacy in these populations are not established.
- Not evaluated for use in the regeneration of alveolar bone or in conjunction with dental implants.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Doxycycline is classified as a Category D drug during pregnancy, indicating evidence of fetal risk. It can cross the placenta and may cause fetal harm, including effects on skeletal development. Therefore, doxycycline should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Doxycycline is excreted into human milk; while the theoretical risks to a nursing infant include dental staining and inhibition of bone growth, these effects are unlikely. Caution is advised when administering doxycycline to breastfeeding women, and alternative treatments should be considered when possible.