Bleomycin
23 June, 2023
Budesonide ER Tablets
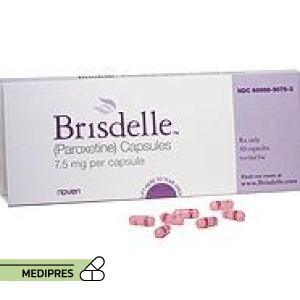
23 June, 2023Brisdelle
Generic name:
Paroxetine
Drug class:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
Dosage form:
Oral capsule, 7.5 mg
Root of administration:
Oral
Dose:
The recommended dose is 7.5 mg once daily at bedtime. Dosage adjustments are not generally required; consult product labeling for special populations.
Mechanism of action:
Paroxetine selectively inhibits the reuptake of serotonin (5-HT) in the central nervous system, increasing serotonin levels in synaptic clefts and modulating hypothalamic thermoregulatory pathways to reduce vasomotor symptoms.
Drug usage cases:
- Approved: Moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (hot flashes) associated with menopause
- Off-label: Major depressive disorder
- Off-label: Generalized anxiety disorder
- Off-label: Panic disorder
- Off-label: Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Drug contra indications:
- Concurrent use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of MAOI discontinuation
- Concurrent use with thioridazine or pimozide
- Known hypersensitivity to paroxetine or any component of the formulation
- Use of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue
Side effects:
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Somnolence or insomnia
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Weight changes
- Sexual dysfunction (e.g., decreased libido, anorgasmia, delayed ejaculation)
- Withdrawal symptoms on abrupt discontinuation
- Increased sweating
- Tremor
- Agitation or hostility
Warnings:
- Increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults
- Serotonin syndrome when used with other serotonergic agents or MAOIs
- Discontinuation syndrome: taper gradually to minimize withdrawal
- Risk of bleeding, especially with NSAIDs, aspirin, or anticoagulants
- Hyponatremia (SIADH), particularly in elderly
- Use with caution in patients with seizure history
- Possible increased risk of bone fractures in postmenopausal women
- Risk of angle-closure glaucoma due to pupillary dilation
- Potential activation of mania or hypomania in bipolar disorder
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Use during pregnancy: Paroxetine crosses the placenta and may be associated with an increased risk of congenital malformations (particularly cardiac defects) and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) with third‐trimester exposure. Use only if the benefit justifies the potential risk. Monitor neonates for withdrawal symptoms following late-term exposure.
Use during breastfeeding: Paroxetine is excreted in human milk. Breastfed infants may experience sedation, feeding difficulties, or weight changes. Consider alternative therapy or monitor the infant closely if breastfeeding.