Brilinta
23 June, 2023
Bupropion
23 June, 2023Bumetanide
Drug class: Loop diuretics
Dosage form: Tablet
Root of administration: Oral
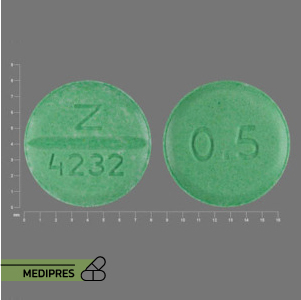
Dose:
- Bumetanide 0.5 mg tablets
- Bumetanide 1 mg tablets
- Bumetanide 2 mg tablets
Mechanism of action: involves blocking the reabsorption of sodium, chloride, and other electrolytes in the kidneys, which leads to increased urine production and removal of excess fluid from the body. This helps to reduce edema and lower blood pressure.
Drug usage cases: Bumetanide is a medication used to treat conditions such as edema (fluid retention) and hypertension (high blood pressure)
Drug contra indications: Bumetanide is contraindicated (should not be used) in the following situations:
- Hypersensitivity: Bumetanide should not be used in individuals who have a known hypersensitivity to the medication or any of its components.
- Severe renal impairment: Bumetanide should not be used in individuals with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) or anuria (lack of urine production).
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Bumetanide should not be used in individuals with hepatic encephalopathy, a severe liver disease that can cause confusion, drowsiness, and other neurological symptoms.
- Electrolyte depletion: Bumetanide should not be used in individuals with electrolyte depletion, such as hypokalemia (low potassium levels), hyponatremia (low sodium levels), or hypovolemia (low blood volume).
Side effects: Some common side effects of bumetanide include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dehydration
- Electrolyte imbalances (such as low potassium levels)
- Muscle cramps or weakness
Warnings: The dose of Bumetanide should be adjusted to the patient’s need. Excessive doses or too frequent administration can lead to profound water loss, electrolyte depletion, dehydration, reduction in blood volume and circulatory collapse with the possibility of vascular thrombosis and embolism, particularly in elderly patients.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. A small investigational experience in the United States and marketing experience in other countries to date have not indicated any evidence of adverse effects on the fetus, but these data do not rule out the possibility of harmful effects. Bumetanide should be given to a pregnant woman only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.