Cefuroxime (Injection, Intravenous)
23 June, 2023
Cetuximab
23 June, 2023Ceta Plus
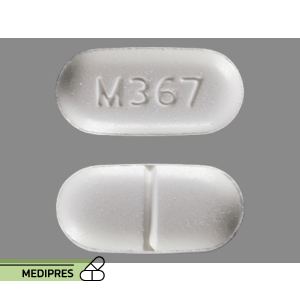
Generic name: hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen
Drug class: Narcotic analgesic combinations
Dosage form: Oral tablet
Root of administration: Oral
Dose:
- Adults: 2.5 to 10 mg hydrocodone every 4 to 6 hours as needed; do not exceed 60 mg per day.
- Children: 0.15 to 0.2 mg/kg hydrocodone every 6 hours as needed; do not exceed 2.5 mg per dose.
Mechanism of action: Hydrocodone is an opioid agonist that binds to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, altering the perception and emotional response to pain. Acetaminophen is a non-opioid analgesic that inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that promote inflammation, pain, and fever.
Drug usage cases:
- Management of moderate to severe pain
- Short-term relief of cough
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to hydrocodone, acetaminophen, or any component of the formulation
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma
- Known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus
- Concurrent use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOIs
Side effects:
- Common: Drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness, and respiratory depression
- Serious: Hypotension, bradycardia, seizures, and allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis
Warnings:
- Risk of addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death
- Respiratory depression may occur; monitor closely, especially during initiation and dose increases
- Use caution in patients with a history of substance abuse, respiratory disorders, or head injury
- Acetaminophen overdose can lead to severe liver damage; do not exceed the recommended daily dose
- Use caution when operating heavy machinery or driving due to potential drowsiness and dizziness
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Hydrocodone is classified as a Category C drug during pregnancy, indicating that risk to the fetus cannot be ruled out. It should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Hydrocodone is excreted in breast milk; therefore, caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman. The decision to use this medication during breastfeeding should be made after careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits.