Fulvestrant
23 June, 2023
Gavreto
23 June, 2023Furosemide
Generic name: furosemide
Brand names: Lasix, Diaqua-2, Lo-Aqua, Furoscix
Drug class: Loop diuretics
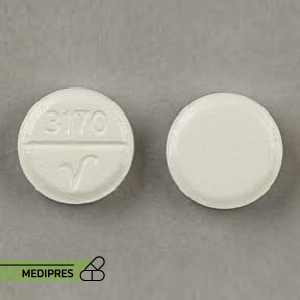
Dosage form: Tablet, injectable solution, oral liquid
Root of administration: oral, injection
Dose: injectable solution (10 mg/mL), intravenous solution (100 mg/100 mL-0.9%), oral liquid (10 mg/mL), oral solution (40 mg/5 mL), oral tablet (20 mg; 40 mg; 80 mg), subcutaneous kit (80 mg/10 mL)
Mechanism of action: Furosemide is a loop diuretic (water pill) that prevents your body from absorbing too much salt. This allows the salt to instead be passed in your urine.
Drug usage cases: Furosemide is used to treat fluid retention (edema) in people with congestive heart failure, liver disease, or a kidney disorder such as nephrotic syndrome. Furosemide is also used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
Drug contraindications: You should not use furosemide if you are allergic to it, if you are unable to urinate or have hepatic cirrhosis. You should not use Furiosi if you have ascites or have allergies to medical adhesives. To make sure furosemide is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had:
- an electrolyte imbalance (such as low levels of potassium or magnesium in your blood)
- enlarged prostate, bladder obstruction, or other urination problems
- gout
- lupus
- diabetes
- an allergy to sulfa drugs
- kidney disease
- cirrhosis or other liver disease.
Side effects: Furosemide may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have:
- a light-headed feeling, like you might pass out
- ringing in your ears, hearing loss
- muscle spasms or contractions
- pale skin, easy bruising, unusual bleeding
- high blood sugar – increased thirst, increased urination, dry mouth, fruity breath odor
- kidney problems – swelling, urinating less, feeling tired or short of breath
- signs of liver or pancreas problems – loss of appetite, upper stomach pain (that may spread to your back), nausea or vomiting, dark urine, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- signs of an electrolyte imbalance – increased thirst or urination, constipation, muscle weakness, leg cramps, numbness or tingling, feeling jittery, fluttering in your chest.
Warnings: You should not use furosemide if you are unable to urinate. Using more than your recommended dose will not make this medicine more effective. High doses of furosemide may cause irreversible hearing loss. Before using furosemide, tell your doctor if you have kidney disease, enlarged prostate, urination problems, cirrhosis or other liver disease, an electrolyte imbalance, high cholesterol, gout, lupus, diabetes, or an allergy to sulfa drugs. Tell your doctor if you have recently had an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or any type of scan using a radioactive dye that is injected into your veins. Do not take more of this medication than is recommended. If you are being treated for high blood pressure, keep using furosemide even if you feel fine. High blood pressure often has no symptoms.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: It is not known if furosemide will harm an unborn baby. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It may not be safe to breastfeed while using furosemide. Ask your doctor about any risk. Furosemide may slow breast milk production.