Harvoni
23 June, 2023
Horizant
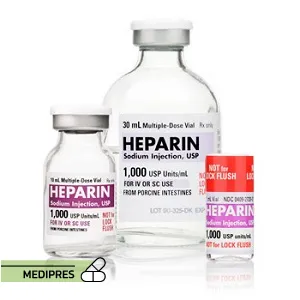
23 June, 2023Heparin
Generic name: heparin (injection) [ HEP-a-rin ]
Brand names: Hep-Pak (obsolete), Heparin Lock Flush (obsolete), Hep-Pak CVC (obsolete), Hep-Lock (obsolete), Heparin Sodium ADD-Vantage
Drug Class: Anticoagulant
Dosage Form: Injectable Solution, Prefilled Syringe
Route of Administration: Intravenous, Subcutaneous
Dose:
- Injectable Solution: Varies widely based on therapeutic or prophylactic use, typically calculated by international units (IU)
- Prefilled Syringe: Commonly available in various doses ranging from 1,000 to 20,000 IU
Mechanism of Action: Heparin works by inhibiting clotting factors, particularly thrombin and factor Xa, leading to decreased formation of fibrin clots. It enhances the activity of antithrombin III, reducing blood’s ability to form clots.
Drug Usage Cases: Heparin is used to prevent and treat blood clots, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). It is also used during certain surgical procedures to prevent clotting.
Drug Contraindications: Contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to heparin, active bleeding, severe thrombocytopenia, or a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
Side Effects: Common side effects include bleeding, bruising, and injection site reactions. Serious side effects may include severe bleeding, thrombocytopenia, and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
Warnings: Regular monitoring of blood clotting parameters is essential to avoid over-anticoagulation and the risk of bleeding. Heparin should be used with caution in patients with bleeding disorders or those taking other anticoagulants.
Use During Pregnancy or Breastfeeding: Heparin is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy, as it does not cross the placenta. It is commonly used for anticoagulation during pregnancy. However, there is limited information on its excretion in human milk; caution should be exercised during breastfeeding.