Kanamycin
23 June, 2023
Keppra
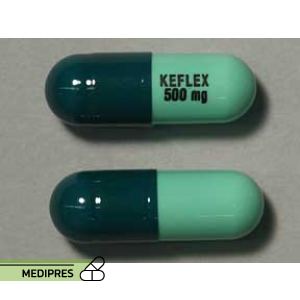
23 June, 2023Keflex
Generic name: Cephalexin
Drug class: First-generation cephalosporin antibiotics
Dosage form: Capsules, tablets, oral suspension
Root of administration: Oral
Dose: Adults: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours, or 500 mg every 12 hours; Children: 25 mg to 50 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into multiple doses
Mechanism of action: Cephalexin inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, leading to bacterial cell lysis and death.
Drug usage cases:
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Ear infections
- Skin infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Bone infections
- Streptococcal pharyngitis
- Cellulitis
- Otitis media
- Acute prostatitis
Drug contra indications:
- Hypersensitivity to cephalexin or other cephalosporin antibiotics
- History of severe allergic reactions to penicillins
- History of cholestatic jaundice or hepatic dysfunction associated with cephalexin use
Side effects:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Indigestion
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Rash
- Vaginal itching or discharge
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Severe allergic reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis)
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea
- Seizures (rare)
- Blood disorders (e.g., thrombocytopenia, leukopenia)
Warnings:
- Use with caution in patients with renal impairment; dose adjustment may be necessary
- Monitor for signs of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea; discontinue if severe diarrhea occurs
- Exercise caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease, particularly colitis
- May cause false-positive results in urine glucose tests; consider alternative testing methods
- Use with caution in patients with a history of penicillin allergy; cross-reactivity may occur
- Monitor for signs of anaphylaxis during the first dose; discontinue immediately if symptoms occur
- Use with caution in elderly patients; may be more susceptible to side effects
- May interact with other medications; inform healthcare provider of all concurrent medications
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Cephalexin is classified as a Category B drug for pregnancy, indicating that it is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy. Limited data suggest that cephalexin does not pose significant risks to the fetus. However, it should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed and prescribed by a healthcare provider. Cephalexin is excreted into human breast milk in small amounts. While the risk to a nursing infant is considered low, caution is advised when administering cephalexin to breastfeeding mothers. It is recommended to consult a healthcare provider before using cephalexin during breastfeeding to assess potential risks and benefits.