Ketoconazole
23 June, 2023
Kevzara
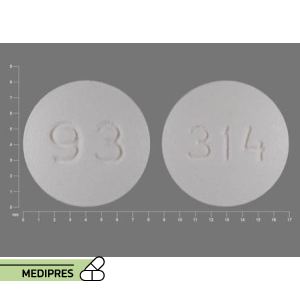
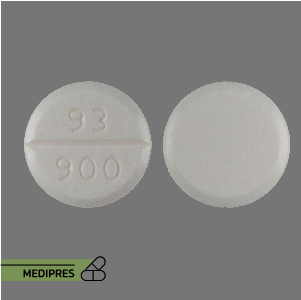
23 June, 2023Ketorolac
Generic name: Ketorolac
Drug class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
Dosage form: Oral tablets, intramuscular injection, intravenous injection, nasal spray, ophthalmic solution
Route of administration: Oral, intramuscular, intravenous, nasal, ophthalmic
Dose:
- Adults: Initial dose of 30 mg intramuscularly or intravenously, followed by 30 mg every 6 hours as needed, not exceeding 120 mg in 24 hours. Oral dosing is initiated with a 20 mg dose after parenteral administration, then 10 mg every 4 to 6 hours, not exceeding 40 mg in 24 hours. Treatment duration should not exceed 5 days due to increased risk of adverse effects.
- Geriatric patients: Caution is advised; lower doses may be necessary due to increased risk of adverse effects.
- Renal impairment: Contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment; use with caution in those with mild to moderate impairment.
Mechanism of action: Ketorolac is a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2) enzymes, leading to decreased synthesis of prostaglandins, which are mediators of pain, inflammation, and fever.
Drug usage cases:
- Short-term management of moderate to severe acute pain, such as postoperative pain.
- Adjunctive therapy to opioids for enhanced pain relief.
- Management of dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation).
- Treatment of idiopathic pericarditis to reduce inflammation.
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to ketorolac or other NSAIDs.
- Active peptic ulcer disease or recent gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Severe renal impairment or patients at risk for renal failure due to volume depletion.
- Patients with a history of asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs.
- During labor and delivery.
- Concurrent use with other NSAIDs or probenecid.
Side effects:
- Common: Drowsiness, dizziness, abdominal pain, swelling, nausea.
- Serious: Gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney failure, heart attacks, bronchospasm, heart failure, anaphylaxis.
- Less common: Paresthesia, prolonged bleeding time, injection site pain, purpura, sweating, abnormal thinking, increased production of tears, edema, pallor, dry mouth, abnormal taste, urinary frequency, increased liver enzymes, itching.
Warnings:
- Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including heart attack and stroke.
- Elevated risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events, such as bleeding, ulceration, and perforation.
- Use is not recommended during the last part of pregnancy or during breastfeeding.
- Use with caution in patients with a history of cardiovascular disease, renal impairment, or gastrointestinal disorders.
- Monitor for signs of bleeding, especially in patients with coagulation disorders or those on anticoagulant therapy.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Pregnancy: Ketorolac is classified as a Category C drug during pregnancy, indicating that risk to the fetus cannot be ruled out. NSAIDs, including ketorolac, may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus, leading to pulmonary hypertension. Therefore, ketorolac should be avoided during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Breastfeeding: Ketorolac is excreted in human milk. While no adverse effects have been reported in breastfed infants, caution is advised. The potential benefits of breastfeeding should be weighed against the risks of administering ketorolac to the mother.