Lacosamide
23 June, 2023
Lantus
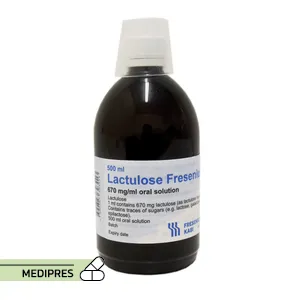
23 June, 2023Lactulose
Generic name: lactulose (oral) [ LAK-too-lose ]
Brand names: Constulose, Generlac, Kristalose, Chronulac, Cephulac, Constilac, Cholac, Duphalac, Evalose, Heptalac, Enulose
Drug class: Laxatives (Osmotic)
Dosage form: Oral solution, Powder for solution
Route of administration: Oral, Rectal
Dosage forms: oral powder for reconstitution (10 g; 20 g), oral syrup (10 g/15 mL), oral and rectal liquid (10 g/15 mL)
Mechanism of action: Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide that is broken down in the colon into lactic acid and other organic acids, increasing osmotic pressure and drawing water into the bowel, resulting in bowel movement.
Drug usage cases: Lactulose is used to treat chronic constipation and to manage hepatic encephalopathy by reducing blood ammonia levels.
Drug contra indications: Lactulose should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug, galactosemia, or intestinal obstruction.
Side effects: Common side effects include flatulence, bloating, and abdominal discomfort. Serious side effects may include:
- Electrolyte imbalance: Risk of low sodium, potassium, and dehydration.
- Severe diarrhea: Potential for severe and prolonged diarrhea.
- Hypernatremia: Elevated sodium levels in the blood.
Warnings: Lactulose can cause significant electrolyte disturbances and dehydration, particularly with prolonged use or in high doses. Regular monitoring of electrolytes is recommended, especially in patients with renal impairment or those taking diuretics.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Lactulose is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is not significantly absorbed systemically, so it is unlikely to affect the fetus or nursing infant.