Mebendazole
23 June, 2023
Medroxyprogesterone
23 June, 2023Meclofenamate
Generic name: Meclofenamate
Drug class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
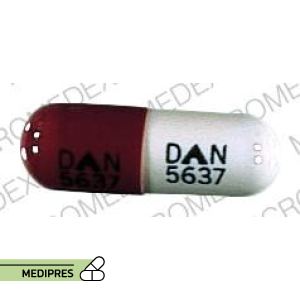
Dosage form: Oral capsules (50 mg, 100 mg)
Root of administration: Oral
Dose:
- Adults and children 14 years and older:
- Pain relief: 50 mg orally every 4 to 6 hours as needed; maximum dose: 400 mg/day
- Primary dysmenorrhea (menstrual pain): 100 mg orally three times a day, starting at the onset of menstrual flow; duration: up to 6 days
- Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: 200 mg to 400 mg orally per day in 3 to 4 divided doses; maximum dose: 400 mg/day
- Pediatric use (children 14 years and older):
- Primary dysmenorrhea: 100 mg orally three times a day, starting at the onset of menstrual flow; duration: up to 6 days
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: 200 mg to 400 mg orally per day in 3 to 4 divided doses; maximum dose: 400 mg/day
Mechanism of action: Meclofenamate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that works by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2), leading to decreased formation of prostaglandins and thromboxanes, which are responsible for pain, inflammation, and fever.
Drug usage cases:
- Relief of mild to moderate pain
- Treatment of primary dysmenorrhea (menstrual pain)
- Management of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
- Reduction of heavy menstrual bleeding
- Management of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in patients 14 years and older
- Relief of shoulder pain caused by bursitis or tendinitis
- Management of ankylosing spondylitis
- Treatment of gouty arthritis
Drug contraindications:
- Known hypersensitivity to meclofenamate or any component of the formulation
- History of asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs
- Active gastrointestinal bleeding or peptic ulcer disease
- Severe renal impairment
- Severe hepatic impairment
- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (due to increased risk of cardiovascular events)
Side effects:
- Gastrointestinal: Indigestion, stomach pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, abdominal cramps, dyspepsia
- Cardiovascular: Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke
- Renal: Fluid retention, swelling, decreased urination
- Hematologic: Anemia, pale skin, unusual tiredness, light-headedness, shortness of breath, cold hands and feet
- Dermatologic: Skin rash, pruritus
- CNS: Dizziness, headache
- Hepatic: Loss of appetite, upper right stomach pain, tiredness, itching, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
Warnings:
- Increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal; risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use
- Contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
- Increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events, including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal; these events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms
- Use with caution in patients with a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or smoking
- Use with caution in patients with a history of stomach ulcers or bleeding, liver or kidney disease, asthma, or fluid retention
- Older adults may be at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events
- Use with caution in patients with a history of asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Meclofenamate is not approved for use by anyone younger than 14 years old. If you are pregnant, you should not take meclofenamate unless your doctor tells you to. Taking an NSAID during the last 20 weeks of pregnancy can cause serious heart or kidney problems in the unborn baby and possible complications with your pregnancy. Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding.