Medrol
23 June, 2023
Metformin
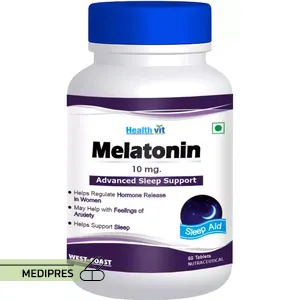
23 June, 2023Melatonin
Generic name: melatonin [ meh-lah-TOE-nin ]
Drug class: Sleep aids (Hormones)
Dosage form: Tablet, Capsule, Liquid, Gummies
Route of administration: Oral
Dose: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg
Mechanism of action: Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. Supplementation increases melatonin levels, helping to induce sleep and regulate circadian rhythms.
Drug usage cases: Melatonin is used for the management of insomnia, jet lag, shift work disorder, and other sleep-related disorders.
Drug contra indications: Melatonin should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to melatonin or any component of the formulation.
Side effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, nausea, and drowsiness. Serious side effects are rare but may include:
- Hormonal effects: Potential effects on puberty, menstrual cycles, and hormone-sensitive conditions.
- Mood changes: Risk of depression or mood swings.
- Allergic reactions: Risk of hypersensitivity reactions.
Warnings: Melatonin can cause drowsiness and impair coordination. Patients should avoid activities requiring mental alertness, such as driving, after taking melatonin. It may interact with other medications, such as anticoagulants and immunosuppressants.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: The safety of melatonin during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well established. It should be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks.