Mephyton
23 June, 2023
Mesalamine Delayed Release Tablets
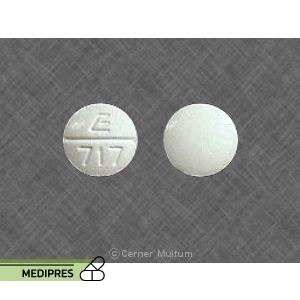
23 June, 2023Meprobamate
Generic name:
Meprobamate
Drug class:
Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant; anxiolytic (carbamate derivative)
Dosage form:
Tablets (200 mg, 400 mg), Oral solution (100 mg/mL)
Route of administration:
Oral
Dose:
Adults: 400–800 mg orally three to four times daily (total up to 5,400 mg/day). Variations by indication and age; consult label.
Elderly: Lower end of dosing range; titrate based on response and tolerability. Pediatric use: Varies by indication; consult label.
Mechanism of action:
Enhances GABAA receptor–mediated inhibitory neurotransmission by binding to an allosteric site, leading to anxiolytic and muscle relaxant effects.
Drug usage cases:
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Tension and muscle spasm
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Off-label: acute musculoskeletal pain
- Off-label: benign essential tremor
- Off-label: temporomandibular joint disorder
Drug contra indications:
- Hypersensitivity to meprobamate, barbiturates, or other carbamates
- Severe respiratory depression or sleep apnea
- Acute or severe hepatic impairment
- Severe renal impairment
- Myasthenia gravis
- Porphyria
Side effects:
- Drowsiness, sedation
- Dizziness, ataxia, impaired coordination
- Headache
- Nausea, vomiting, constipation
- Skin reactions: rash, urticaria
- Cognitive impairment, confusion, depression
- Hypotension, bradycardia
- Respiratory depression (especially at high doses or with CNS depressants)
- Dependence, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms (e.g., tremors, seizures)
- Blood dyscrasias (rare)
Warnings:
- Risk of dependence, abuse, and tolerance; limit duration of therapy
- Abrupt discontinuation may precipitate withdrawal (e.g., restlessness, seizures)
- Use with caution in respiratory disease and hepatic or renal impairment
- May impair mental and/or physical abilities; avoid driving or hazardous tasks
- Additive CNS depression with alcohol, opioids, sedatives, and other depressants
- Use caution in elderly and debilitated patients due to increased sensitivity
- Monitor for signs of misuse, abuse, and diversion
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Pregnancy: Category D. Evidence of human fetal risk exists. Use only if potential benefit justifies the potential risk. Associated with congenital malformations and neonatal withdrawal.
Breastfeeding: Excreted in breast milk; may cause sedation or respiratory depression in the infant. Weigh benefits of breastfeeding against maternal need for treatment and potential adverse effects.