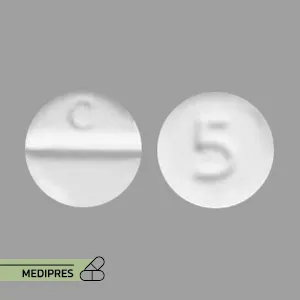
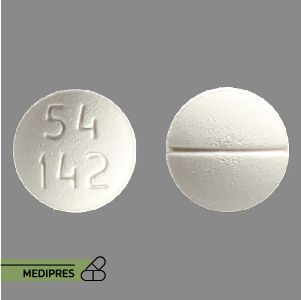
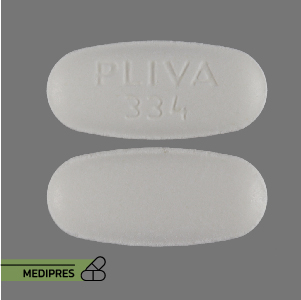
Mycophenolic Acid Tablets
23 June, 2023
Nalbuphine
23 June, 2023Mysoline
Generic name: Primidone
Drug class: Barbiturate anticonvulsants
Dosage form: Oral tablet (50 mg, 125 mg, 250 mg)
Root of administration: Oral
Dose: For adults and children aged 8 years and older with no prior treatment:
– Days 1 to 3: 100 to 125 mg at bedtime.
– Days 4 to 6: 100 to 125 mg twice a day.
– Days 7 to 9: 100 to 125 mg three times a day.
– Day 10 to maintenance: 250 mg three times a day.
Maintenance dosage typically ranges from 750 mg to 1,500 mg per day, divided into three or four doses. The maximum daily dosage should not exceed 2,000 mg.
Mechanism of action: Primidone’s exact mechanism of action is not fully understood. It is believed to raise seizure thresholds by interacting with voltage-gated sodium channels, inhibiting high-frequency repetitive firing of action potentials. Its active metabolites, phenobarbital and phenylethylmalonamide (PEMA), also contribute to its anticonvulsant effects.
Drug usage cases:
- Control of grand mal (tonic-clonic) seizures
- Management of psychomotor (complex partial) seizures
- Treatment of focal (partial) seizures
- Adjunctive therapy for generalized tonic-clonic seizures refractory to other anticonvulsants
- Off-label use for essential tremor
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to phenobarbital or primidone
- Porphyria
Side effects:
- Drowsiness
- Ataxia (lack of muscle coordination)
- Visual disturbances
- Nystagmus (involuntary eye movement)
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability
- Impotence
- Sexual dysfunction
- Rare: Anemia (including megaloblastic anemia), agranulocytosis, and aplastic anemia
- Rare: Dermatological reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Rare: Hepatic dysfunction
- Rare: Osteomalacia (softening of the bones)
- Rare: Dupuytren’s contracture (a condition causing the fingers to bend towards the palm)
Warnings:
- Risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors; monitor for mood changes
- Potential for drowsiness and impaired coordination; caution when driving or operating machinery
- Risk of withdrawal seizures if discontinued abruptly; taper dosage gradually under medical supervision
- May cause drowsiness; avoid alcohol and other CNS depressants
- Use with caution in patients with hepatic or renal impairment
- Monitor for signs of blood dyscrasias (e.g., unexplained bleeding or bruising)
- May cause vitamin D deficiency leading to bone disorders; consider supplementation
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Primidone is classified as a Category D medication during pregnancy, indicating a risk to the fetus. It should only be used if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk. Primidone is excreted in breast milk; caution is advised when administering to nursing mothers. Consult a healthcare provider to discuss potential risks and benefits.