Nadolol
23 June, 2023
Naproxen
23 June, 2023Naloxone
Generic name: naloxone [ nah-LOX-one ]
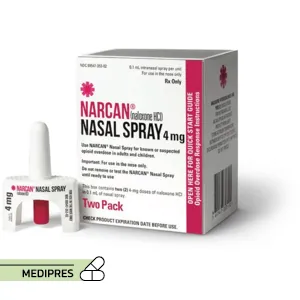
Brand names: Narcan, Kloxxado, Zimhi
Drug class: Opioid antagonist
Dosage form: Injection, Nasal spray, Auto-injector
Route of administration: Intravenous (IV), Intramuscular (IM), Subcutaneous (SubQ), Intranasal
Available Dose:
- Injection: 0.4 mg/mL, 1 mg/mL
- Nasal spray: 4 mg/0.1 mL
- Auto-injector: 2 mg/0.4 mL, 0.4 mg/0.4 mL
Mechanism of action: Naloxone works by competitively binding to opioid receptors in the central nervous system (CNS), displacing opioid molecules and reversing or preventing the effects of opioid drugs, including respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension.
Drug usage cases: Naloxone is used for the emergency treatment of known or suspected opioid overdose, as manifested by respiratory and/or CNS depression. It is also used to diagnose suspected acute opioid overdose and in cases of septic shock.
Drug contraindications: There are no absolute contraindications for the use of naloxone in an emergency situation. Hypersensitivity to naloxone or any of its components should be noted but is extremely rare.
Side effects: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, and injection site reactions. When administered to opioid-dependent individuals, it can precipitate withdrawal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, sweating, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, and agitation.
Warnings: Naloxone should be administered with caution in patients with cardiovascular disease or those receiving medications with potential adverse cardiovascular effects, as serious side effects such as ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, pulmonary edema, and cardiac arrest have been reported. Monitor patients for re-emergence of opioid overdose symptoms, as the duration of action of some opioids may exceed that of naloxone.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Naloxone is categorized as a pregnancy category B drug. It should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Naloxone does not readily cross the placenta, so the risk to the fetus is minimal. It is unknown if naloxone is excreted in human milk; caution should be exercised when administered to breastfeeding women.
Naloxone is a critical medication in opioid overdose management due to its ability to rapidly reverse life-threatening symptoms of opioid toxicity. Its availability in various forms makes it accessible for use by both healthcare professionals and laypersons in emergency situations.