Neomycin
23 June, 2023
Nexplanon
23 June, 2023Nexletol
Generic name: bempedoic acid
Drug class: ATP citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitors
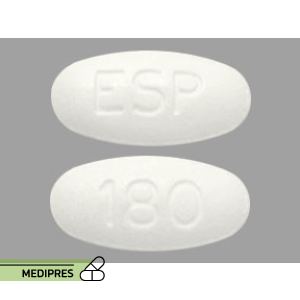
Dosage form: 180 mg oral tablets
Route of administration: Oral
Dose: 180 mg once daily, taken with or without food
Mechanism of action: Bempedoic acid inhibits ATP citrate lyase, an enzyme involved in cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver, leading to reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels. It also upregulates LDL receptors, enhancing the clearance of LDL-C from the bloodstream.
Drug usage cases:
- Adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) who require additional lowering of LDL-C.
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to bempedoic acid or any component of the formulation.
- Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases.
- Concomitant use with simvastatin doses greater than 20 mg or pravastatin doses greater than 40 mg due to increased risk of myopathy.
Side effects:
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Muscle spasms
- Hyperuricemia
- Back pain
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Bronchitis
- Pain in extremity
- Anemia
- Elevated liver enzymes
Warnings:
- Elevations in serum uric acid have occurred; monitor uric acid levels periodically and assess for signs and symptoms of hyperuricemia.
- Tendon rupture has occurred; discontinue bempedoic acid at the first sign of tendon rupture and avoid use in patients with a history of tendon disorders or tendon rupture.
- Use with caution in patients with a history of gout or at risk for hyperuricemia.
- Monitor liver function tests before initiating therapy and periodically thereafter; discontinue if persistent elevations occur.
- Concomitant use with simvastatin doses greater than 20 mg or pravastatin doses greater than 40 mg is contraindicated due to increased risk of myopathy.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
It is not recommended to use bempedoic acid during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Discontinue bempedoic acid when pregnancy is recognized, unless the benefits of therapy outweigh the potential risks to the fetus. Based on the mechanism of action, bempedoic acid may cause fetal harm. It is not known whether bempedoic acid is excreted in human milk; therefore, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment.