Palgic
23 June, 2023
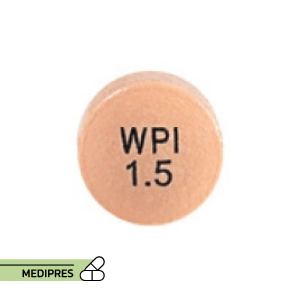
Panixine DisperDose
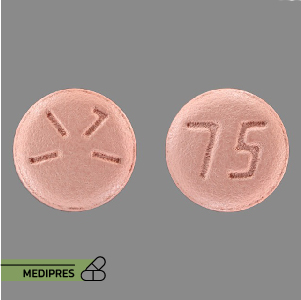
23 June, 2023Paliperidone (Oral)
Generic name: Paliperidone
Drug class: Atypical antipsychotic
Dosage form: Extended-release oral tablet
Route of administration: Oral
Dose:
- Adults (Schizophrenia): Initial dose of 6 mg once daily in the morning; maintenance dose ranges from 3 mg to 12 mg once daily, adjusted based on clinical response. The maximum recommended dose is 12 mg per day.
- Adults (Schizoaffective Disorder): Initial dose of 6 mg once daily in the morning; maintenance dose ranges from 3 mg to 12 mg once daily, adjusted based on clinical response. The maximum recommended dose is 12 mg per day.
- Adolescents (12 to 17 years, weighing 51 kg or more): Initial dose of 3 mg once daily in the morning; maintenance dose ranges from 3 mg to 12 mg once daily, adjusted based on clinical response. The maximum recommended dose is 12 mg per day.
- Adolescents (12 to 17 years, weighing less than 51 kg): Initial dose of 3 mg once daily in the morning; maintenance dose ranges from 3 mg to 6 mg once daily, adjusted based on clinical response. The maximum recommended dose is 6 mg per day.
- Children under 12 years: Use and dose must be determined by a healthcare provider.
Mechanism of action: Paliperidone is the active metabolite of risperidone. It exerts its antipsychotic effects by antagonizing dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in the brain, which helps to balance neurotransmitter activity and alleviate symptoms associated with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Drug usage cases:
- Treatment of schizophrenia in adults and adolescents aged 12 to 17 years.
- Treatment of schizoaffective disorder in adults.
- Adjunctive therapy for schizoaffective disorder in adults, in combination with mood stabilizers and/or antidepressants.
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to paliperidone, risperidone, or any component of the formulation.
- Severe central nervous system depression.
- Comatose states.
- Concurrent use with other antipsychotic agents without appropriate medical supervision.
Side effects:
- Common: Headache, insomnia, sleepiness, parkinsonism (e.g., tremor, muscle stiffness), dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions), dizziness, akathisia (restlessness), agitation, anxiety, depression, weight gain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dyspepsia (heartburn), diarrhea, dry mouth, fatigue, toothache, muscle and bone pain, back pain, asthenia (weakness), tachycardia (increased heart rate), high blood pressure, prolonged QT interval, upper respiratory tract infection, and cough.
- Less common: Seizures, severe constipation, severe vomiting, stomach pain, swollen tongue, yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), and sleepwalking.
Warnings:
- Use with caution in patients with a history of heart disease, including heart attack, heart failure, or arrhythmias.
- Monitor for signs of tardive dyskinesia, a potentially irreversible movement disorder.
- Use cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or epilepsy.
- Monitor for signs of neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a rare but serious condition characterized by hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and autonomic dysregulation.
- Use with caution in patients with a history of diabetes or those at risk for hyperglycemia, as paliperidone may increase blood sugar levels.
- Monitor for signs of hyperprolactinemia, which can lead to galactorrhea, gynecomastia, and menstrual disturbances.
- Use cautiously in elderly patients, especially those with dementia-related psychosis, due to an increased risk of death.
- Use with caution in patients with renal or hepatic impairment; dose adjustments may be necessary.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: Paliperidone is classified as a Category C medication during pregnancy, indicating that risk to the fetus cannot be ruled out. It should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Paliperidone is excreted in human milk; caution should be exercised when administering to a nursing woman. The decision to discontinue nursing or the drug should be made based on the importance of the drug to the mother and the potential risks to the nursing infant.