Pantothenic acid
23 June, 2023
Pemetrexed
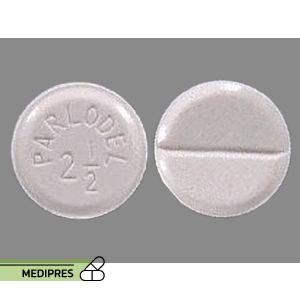
23 June, 2023Parlodel
Category: P
Description
Generic name:
Bromocriptine mesylate
Drug class:
Dopamine D2 receptor agonist; ergot derivative
Dosage form:
- Tablets: 0.5 mg, 2.5 mg
Root of administration:
Oral
Dose:
- Hyperprolactinemia: Initial 1.25 mg once daily; increase by 1.25 mg weekly up to 1.25–2.5 mg two to three times daily (max 15 mg/day).
- Parkinson’s disease: 1.25 mg once daily; may increase gradually to 30 mg/day in divided doses.
- Acromegaly: Start 1.25 mg daily; titrate up to 15–30 mg/day.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (adjunct): 0.8 mg once daily within 2 hours of waking.
- Postpartum lactation suppression: 2.5 mg twice daily for 14 days.
- Off-label uses: Varies by indication; consult label.
Mechanism of action:
Bromocriptine is a dopamine D2 receptor agonist that inhibits prolactin secretion from the anterior pituitary and exerts central dopaminergic effects.
Drug usage cases:
- Hyperprolactinemia (e.g., prolactin-secreting pituitary adenoma)
- Parkinson’s disease
- Acromegaly
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (adjunct therapy)
- Postpartum lactation suppression
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (off-label)
- Restless legs syndrome (off-label)
Drug contra indications:
- Hypersensitivity to ergot alkaloids or bromocriptine
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Preeclampsia or eclampsia
- History of stroke or myocardial infarction within 6 months
- Psychotic disorders
- Active peptic ulcer disease
- Breastfeeding or intended to breastfeed
- Severe hepatic impairment
Side effects:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Headache, dizziness
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Fatigue, somnolence
- Nasal congestion
- Constipation, abdominal cramps
- Depression, anxiety
- Hallucinations, psychosis
- Peripheral edema
- Valvular heart disease
- Pulmonary fibrosis, pleural effusion
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
Warnings:
- Monitor blood pressure for hypotension
- Risk of cardiac valvulopathy; periodic echocardiograms recommended
- Potential for fibrotic complications (pulmonary, retroperitoneal, cardiac)
- May cause excessive somnolence or sudden sleep episodes
- Psychiatric events: hallucinations, impulse control disorders
- Monitor liver function in hepatic impairment
- Abrupt withdrawal may cause rebound hyperprolactinemia
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Pregnancy: Category B. Animal studies show no teratogenicity; limited human data. Use only if clearly needed; monitor patient closely. Bromocriptine may inhibit lactation and has been used to suppress postpartum lactation; avoid if breastfeeding is desired.
Breastfeeding: Contraindicated as it suppresses milk production and is excreted in breast milk; not recommended.