Propranolol
23 June, 2023
Qalsody
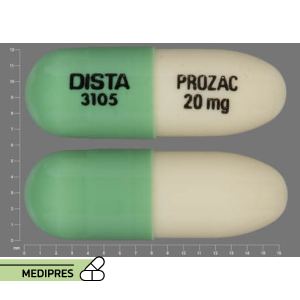
23 June, 2023Prozac
Generic name: Fluoxetine
Drug class: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Dosage form: Capsules (10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg), delayed-release capsules (90 mg), tablets (10 mg, 20 mg, 60 mg), oral solution (20 mg/5 mL)
Route of administration: Oral
Dose: For major depressive disorder in adults: 20 mg once daily, which may be increased to a maximum of 80 mg per day. For obsessive-compulsive disorder in adults: 20 mg once daily, with possible increases up to 60 mg per day. For bulimia nervosa in adults: 60 mg once daily. For panic disorder in adults: 10 mg once daily, increased to 20 mg after one week, with a maximum of 60 mg per day. For premenstrual dysphoric disorder in adults: 20 mg once daily. For major depressive disorder in children and adolescents (8 years and older): 10 mg once daily, increased to 20 mg after one week, with a maximum of 20 mg per day. For obsessive-compulsive disorder in children and adolescents (7 years and older): 10 mg once daily, increased to 20 mg after one week, with a maximum of 20 mg per day. For bulimia nervosa in adolescents: 60 mg once daily. For panic disorder in adolescents: 10 mg once daily, increased to 20 mg after one week, with a maximum of 20 mg per day. For premenstrual dysphoric disorder in adolescents: 20 mg once daily. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for patients with hepatic impairment. The delayed-release formulation (Prozac Weekly) is taken once weekly, with a typical dose of 90 mg.
Mechanism of action: Fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that increases serotonin levels in the brain by inhibiting its reuptake into presynaptic neurons, thereby enhancing serotonergic neurotransmission and improving mood and anxiety symptoms.
Drug usage cases:
- Major depressive disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Bulimia nervosa
- Panic disorder
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder
- Depressive episodes associated with bipolar I disorder (when used with olanzapine)
- Treatment-resistant depression (when used with olanzapine)
- Premature ejaculation (off-label)
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to fluoxetine or any component of the formulation
- Concurrent use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of discontinuing an MAOI
- Concurrent use with pimozide
- Concurrent use with thioridazine
- Concurrent use with linezolid
- Concurrent use with methylene blue injection
Side effects:
- Common: Nausea, insomnia, headache, dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, increased sweating, tremor, sexual dysfunction (e.g., decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, anorgasmia), weight loss, diarrhea, fatigue, anxiety, nervousness, yawning, decreased appetite, and sleep disturbances.
- Serious: Serotonin syndrome (symptoms may include agitation, hallucinations, rapid heartbeat, high or low blood pressure, fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tremor, muscle rigidity, dizziness, seizures, and coma), QT interval prolongation, hyponatremia, bleeding abnormalities, angle-closure glaucoma, and suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
Warnings:
- Increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, adolescents, and young adults; monitor closely for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts.
- Serotonin syndrome risk, especially when combined with other serotonergic agents.
- QT interval prolongation; use caution in patients with a history of QT prolongation or concurrent use of QT-prolonging drugs.
- Hyponatremia; monitor sodium levels, particularly in elderly patients.
- Bleeding risk; caution in patients taking anticoagulants or with a history of bleeding disorders.
- Angle-closure glaucoma; monitor for visual disturbances and eye pain.
- Discontinuation syndrome; taper dosage gradually to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
- Use with caution in patients with a history of seizures; may lower the seizure threshold.
- May impair cognitive and motor performance; use caution when driving or operating machinery until individual response is known.
- Alcohol may enhance the sedative effects; avoid alcohol consumption during treatment.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Pregnancy: Fluoxetine is classified as a Category C drug by the FDA, indicating that risk to the fetus cannot be ruled out. Studies in animals have shown adverse effects, but there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Use during pregnancy should be considered only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Neonates exposed to SSRIs, including fluoxetine, during the third trimester have been reported to experience complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. These complications may arise immediately upon delivery.
Breastfeeding: Fluoxetine is excreted in human milk. The American Academy of Pediatrics considers fluoxetine compatible with breastfeeding, but caution is advised due to potential side effects in the nursing infant. Monitor the infant for adverse effects such as irritability, drowsiness, or feeding difficulties. Consult a healthcare provider before initiating treatment during breastfeeding.