Tasmar
23 June, 2023
Tecfidera
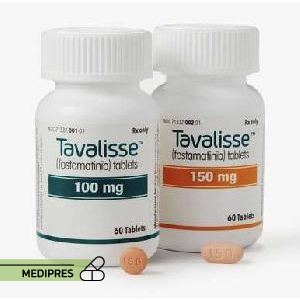
23 June, 2023Tavalisse
Generic name: fostamatinib
Drug class: Miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
Dosage form: Oral tablets (100 mg and 150 mg)
Route of administration: Oral
Dose: Initial dose: 100 mg orally twice daily; after 4 weeks, if platelet count has not increased to at least 50 × 10⁹/L, increase to 150 mg orally twice daily. Use the lowest dose necessary to achieve and maintain a platelet count of at least 50 × 10⁹/L to reduce the risk of bleeding.
Mechanism of action: Fostamatinib is a spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) inhibitor that blocks the SYK enzyme, reducing the immune system’s destruction of platelets, thereby increasing platelet counts and decreasing the risk of bleeding.
Drug usage cases:
- Treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) in adults who have had an insufficient response to previous treatments.
Drug contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to fostamatinib or any component of the formulation.
- Active bleeding disorders.
- Severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C).
- Uncontrolled hypertension.
- Pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding.
Side effects:
- Common: Diarrhea, hypertension, nausea, respiratory infection, dizziness, increased liver enzymes (ALT, AST), rash, abdominal pain, fatigue, chest pain, decreased white blood cell count (neutropenia).
- Serious: Severe diarrhea, liver dysfunction (e.g., jaundice, dark urine), significant hypertension, infections.
Warnings:
- Monitor blood pressure regularly; Tavalisse can cause significant increases in blood pressure.
- Monitor liver function tests monthly; Tavalisse can cause elevations in liver enzymes.
- Monitor complete blood counts regularly; Tavalisse can cause decreases in white blood cell counts.
- Discontinue Tavalisse if platelet count does not increase to at least 50 × 10⁹/L after 12 weeks of treatment.
- Use caution in patients with a history of hypertension, liver disease, or infections.
- Patients should avoid contact with individuals who have infections that may spread to others.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Fostamatinib can harm an unborn baby. Females who can become pregnant should use effective birth control during treatment and for at least 1 month after the last dose. It is not known if fostamatinib passes into breast milk; therefore, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment and for at least 1 month after the last dose.