Teriflunomide
23 June, 2023
Testosterone injection
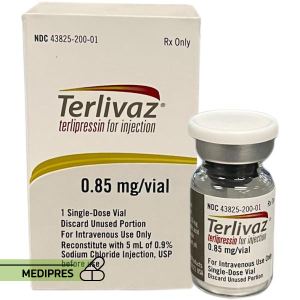
23 June, 2023Terlivaz
Generic name: terlipressin
Drug class: Antidiuretic hormones
Dosage form: Powder for solution for injection
Route of administration: Intravenous (IV) injection
Dose: 0.85 mg (1 vial) IV every 6 hours for the first 3 days. If serum creatinine (SCr) decreases by ≥30% from baseline, continue the same dose. If SCr decreases by <30% from baseline, increase the dose to 1.7 mg (2 vials) IV every 6 hours. Treatment continues until 24 hours after two consecutive SCr values ≤1.5 mg/dL at least 2 hours apart or for a maximum of 14 days.
Mechanism of action: Terlipressin is a synthetic vasopressin analogue that acts as a prodrug for lysine-vasopressin. It has a higher selectivity for vasopressin V1 receptors, particularly in the splanchnic circulation, leading to vasoconstriction and increased mean arterial pressure.
Drug usage cases:
- Improvement of kidney function in adults with hepatorenal syndrome with rapid reduction in kidney function.
Drug contraindications:
- Hypoxia or worsening respiratory symptoms.
- Ongoing coronary, peripheral, or mesenteric ischemia.
Side effects:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Respiratory failure
- Diarrhea
- Dyspnea
- Chest pain or pressure
- Hypoxia symptoms (e.g., restlessness, headache, confusion, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, anxiety, or breathing problems)
- Blue-colored appearance in skin, lips, fingers, or toes
- Light-headedness, like fainting
- Pain in arms or legs
- Numbness or tingling in hands or feet
- Bloody or tarry stools
- Weight gain or swelling in arms or legs
Warnings:
- Serious or fatal respiratory failure: Assess oxygenation saturation before initiating treatment. Do not initiate in hypoxic patients until oxygenation levels improve. Monitor for hypoxia during treatment and discontinue if SpO₂ decreases below 90%.
- Ineligibility for liver transplant: Adverse reactions may make a patient ineligible for liver transplantation. For patients with high prioritization for liver transplantation (e.g., MELD ≥35), the benefits may not outweigh the risks.
- Ischemic events: May cause cardiac, cerebrovascular, peripheral, or mesenteric ischemia. Avoid use in patients with a history of severe cardiovascular conditions or cerebrovascular or ischemic disease. Discontinue in patients who experience signs or symptoms suggestive of ischemic adverse reactions.
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: May cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. If used during pregnancy, inform the patient of the potential risk to the fetus.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Terlipressin may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. If terlipressin is used during pregnancy, the patient should be informed of the potential risk to the fetus.