Zonisamide
23 June, 2023
Zyprexa
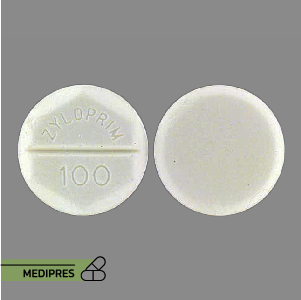
23 June, 2023Zyloprim
Generic name: Allopurinol
Drug class: Antigout agents, Antihyperuricemic agents
Dosage forms: Tablet, Suspension
Root of administration: Oral
Dose: 100, 200, 300 mg
Mechanism of action: Allopurinol is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor that works by decreasing the uric acid produced by the body.
Drug usage cases: Allopurinol is used to prevent or lower high uric acid levels in the blood. It is also used to prevent or lower excess uric acid levels caused by cancer medicines or in patients with kidney stones.
Drug contra indications: In deciding to use a medicine, the risks of taking the medicine must be weighed against the good it will do. This is a decision you and your doctor will make. For this medicine, the following should be considered:
Allergies: Tell your doctor if you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to this medicine or any other medicines. Also tell your health care professional if you have any other types of allergies, such as to foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals. For non-prescription products, read the label or package ingredients carefully. Pediatric: Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated pediatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of allopurinol in children with high uric acid levels caused by cancer. Geriatric: No information is available on the relationship of age to the effects of allopurinol in geriatric patients. Interactions with Medicines: Although certain medicines should not be used together at all, in other cases two different medicines may be used together even if an interaction might occur. In these cases, your doctor may want to change the dose, or other precautions may be necessary. When you are taking this medicine, it is especially important that your healthcare professional know if you are taking any of the medicines listed below. The following interactions have been selected on the basis of their potential significance and are not necessarily all-inclusive. Using this medicine with any of the following medicines is not recommended. Your doctor may decide not to treat you with this medication or change some of the other medicines you take. Didanosine: Using this medicine with any of the following medicines is usually not recommended, but may be required in some cases. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
Acenocoumarol, Azathioprine, Capecitabine, Captopril, Enalapril, Enalaprilat, Fluorouracil, Levoketoconazole, Mercaptopurine, Methotrexate, Pegloticase, Phenprocoumon, Tegafur, Warfarin Using this medicine with any of the following medicines may cause an increased risk of certain side effects, but using both drugs may be the best treatment for you. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
Aluminum Hydroxide, Cyclosporine, Vidarabine. Interactions with Food/Tobacco/Alcohol: Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or eating certain types of food since interactions may occur. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines may also cause interactions to occur. Discuss with your healthcare professional the use of your medicine with food, alcohol, or tobacco. Other Medical Problems: The presence of other medical problems may affect the use of this medicine. Make sure you tell your doctor if you have any other medical problems, especially: Bone marrow problems, Liver disease—Use with caution. May make these conditions worse. Cancer (eg, multiple myeloma), Congestive heart disease, Diabetes, Hypertension (high blood pressure), Hyperuricemia (high uric acid level in the blood) or Kidney problems, chronic (eg, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis)—Use with caution. May cause side effects to become worse. Kidney disease—Use with caution. The effects may be increased because of slower removal of the medicine from the body.
Side effects: Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur:
Ankle, knee, or great toe joint pain, joint stiffness or swelling, rash, rash with flat lesions or small raised lesions on the skin.
Warnings: Hypersensitivity reactions: Zyloprim can rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. These reactions can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Seek medical help if you experience severe skin rash, blistering, peeling, or other signs of an allergic reaction. Liver and kidney function: Zyloprim is primarily eliminated from the body through the kidneys. Individuals with impaired kidney function may require dosage adjustments. Additionally, Zyloprim can rarely cause liver function abnormalities. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function may be necessary, especially in patients with pre-existing liver or kidney disease. Hypersensitivity to other medications: There is a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions to Zyloprim in individuals who have previously experienced hypersensitivity to other medications, such as thiazide diuretics or sulfonylureas. Inform your healthcare provider of any known drug allergies or hypersensitivities. Drug interactions: Zyloprim may interact with other medications, including warfarin (an anticoagulant), azathioprine, and mercaptopurine (immunosuppressants). These interactions can lead to increased or decreased effects of the drugs involved. Inform your healthcare provider about all the medications, supplements, and herbal products you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding: There are no adequate studies in women for determining infant risk when using this medication during breastfeeding. Weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks before taking this medication while breastfeeding. Zyloprim should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed and after careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits.